AR and VR are reforming education by offering an immersive, interactive learning environment that goes beyond conventional methods. The technologies enable students to explore sophisticated concepts through 3D visualization, hands-on simulations, and realistic virtual experiences. AR brings digital information into the real world, enhancing classroom activities, while VR transports learners into fully immersive environments for deeper understanding.
Together, they enhance engagement, knowledge, retention, and personalized learning. With continuous development, AR and VR tools are setting the stage for a new frontier in education where learning will be more experiential, accessible, and future-focused for students around the world.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding AR and VR in Modern Education
- Key Differences Between AR and VR Learning Experiences
- How AR Enhances Real-World Learning
- How VR Creates Fully Immersive Educational Environments
- Benefits of AR and VR for Students and Educators
- AR and VR Tools Transforming Today’s Classrooms
- The Role of AR/VR in Personalized and Adaptive Learning
- Challenges and Limitations of AR and VR in Education
- Future Trends Driving AR/VR Innovations in Learning
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
The landscape of education is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by rapid advancements in immersive technologies, specifically Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). As schools, universities, and training institutions seek innovative ways to prepare learners for the demands of a digital-first world, AR and VR stand out as groundbreaking solutions that elevate learning far beyond traditional methods.
In 2025 and beyond, learning is no longer confined to textbooks, static diagrams, or passive lectures. Instead, the next evolution of education focuses on active, experiential, and immersive learning experiences. AR and VR enable students to step inside complex concepts, explore environments that are otherwise inaccessible, and interact with learning materials in ways that feel natural, intuitive, and memorable. These technologies bridge the gap between imagination and reality, turning abstract ideas into concrete experiences.
From medical students practicing surgeries in lifelike virtual operating rooms to history learners walking through ancient civilizations, AR and VR allow education to transcend physical limitations. Their true power lies in enhancing engagement, deepening understanding, and supporting diverse learning styles. As these technologies continue to advance and become more affordable, they are reshaping the future of learning, offering endless possibilities across classrooms, workplaces, and global education systems.
2. Understanding AR and VR in modern education
To appreciate how AR and VR are revolutionizing learning, it’s important to understand what these technologies are and how they function in educational contexts.
What is Augmented Reality?
AR overlays digital content such as images, animations, or data onto the real world. Through devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses, students can view enhanced real-world environments supplemented with interactive 3D elements or information.
In classrooms, AR might:
- Display a 3D beating heart during biology lessons
- Bring historical figures to life through animated overlays
- Turn a simple worksheet into an interactive learning platform
AR enhances real-world experiences by adding layers of information, making learning more vivid and accessible.
What is Virtual Reality?
VR immerses users in a fully digital environment through a headset. Unlike AR, which blends digital and real worlds, VR transports learners into a simulated space where they can move, interact, and engage as though they are physically present.
In education, it may include:
- Virtual field trips to space, underwater worlds, or ancient civilizations
- 3D Lab simulations for conducting experiments without physical material.
- Skill training environments range from flight simulations to engineering workshops.
VR replaces the physical world entirely, enabling high-impact learning experiences that would otherwise be impossible, dangerous, or expensive.
Immersive Education Takes Center Stage
As digital-native learners increasingly expect dynamic and interactive experiences, AR and VR provide the tools needed to meet these expectations. They support inquiry-based learning, project-based learning, and experiential education approaches proven to improve understanding and retention.
Immersive technologies are becoming integral to education because they:
- Enhance engagement
- Improve practical skills
- Support personalized learning pathways
- Safe and controlled learning environments are provided.
- Encourage exploration and curiosity
Together, AR and VR mark the next chapter of human-centered learning innovation.
3. Key Difference between AR and VR Learning Experiences
While AR and VR both improve educational experiences, they serve different purposes and offer unique types of learning interactions.
1) Level of Immersion
AR: Partially immersive; learners remain tied to the real world.
VR: Completely immersive; learners are placed in a completely different environment.
2) Instruments and Equipment
AR: Smartphones, tablets, AR glasses.
VR: Headsets, controllers, motion sensors, and specialized software.
3) Learning Applications
AR is best for:
- Enhancing physical materials
- Visualizing 3-D content
- On-the-spot learning interactions
- Classroom-based blended learning
VR is ideal for:
- Simulations and virtual labs
- Skill-based training
- High-risk or hard-to-reach experiences
- Full immersion and extensive study sessions
4) Cost and Accessibility
AR: It requires less sophisticated equipment, making it more accessible for schools.
VR: It can be more expensive to set up but offers a richer experiential value.
5) Learning Style Support
AR: It strengthens conceptual understanding and real-time visualization.
VR: It offers hands-on practice, exploration, and experience-oriented learning.
Together, AR and VR create a balanced ecosystem of immersive education, each complementing the other to create meaningful, multi-dimensional learning experiences.
4. How AR is Amplifying Real-World Learning
AR’s primary strength lies in its ability to enhance and enrich the world learners already see. Instead of removing students from their environment, AR adds layers of digital information, transforming physical spaces into interactive learning zones.
Real-time object interaction
AR enables students to examine digital 3D models of objects directly on their desks, whether it’s a molecule, a human anatomy structure, or a mechanical engine. They can rotate models, zoom in, view labels, and observe animations that explain their functions.
Enhanced Textbooks and Worksheets
Printed materials come to life with AR-enabled content. A traditional geography map can display animated weather patterns, while a worksheet can show interactive problem-solving steps.
In-Classroom Exploration
AR helps teachers create interactive lessons with minimal hardware. Students can:
- Scan flashcards to view digital animals
- View historical landmarks in 3D
- Learn about solar system planets floating over their desks.
- Improved Collaboration
Because AR works in a shared environment, multiple students can participate in collaborative learning activities simultaneously.
Contextual Learning
AR delivers information exactly where it is needed. Example:
- Medical students practice mannequins and see the anatomy layered together.
- Engineering students visualize load distributions on real structures
- AR turns the real classroom into a dynamic learning environment, making knowledge more tangible and easier to grasp.
5. How VR Creates Fully Immersive Educational Environments
VR takes immersion to the next level by replacing the learner’s surroundings with a fully digital world. This provides powerful opportunities for hands-on and experiential learning.
Immersive Virtual Field Trips
Students can be referred to:
- Ancient Rome
- Coral reefs
- Mars surface
- Human bloodstream
These immersive trips offer experiences that no number of textbooks or videos can replicate.
Danger-Free Training Simulations
VR provides safe environments to practice the following skills:
- Operative procedures
- Welding, building, and mechanical activities
- Aviation and navigation
- Emergency response training
The controlled VR environment allows for repeated practice without risk.
Increased Focus and Engagement
Because VR blocks external distractions, learners are fully present in the experience, improving concentration and retention.
Learning by Exploring
VR encourages curiosity by enabling students to explore digital worlds, interact with elements, and learn at their own pace.
Psychological Safety to Experiment
Students gain confidence as they practice skills without fear of failure. Mistakes become learning opportunities rather than setbacks.
VR brings experiential learning closer to real-world scenarios than any other educational tool, making it invaluable for both academic and professional training.
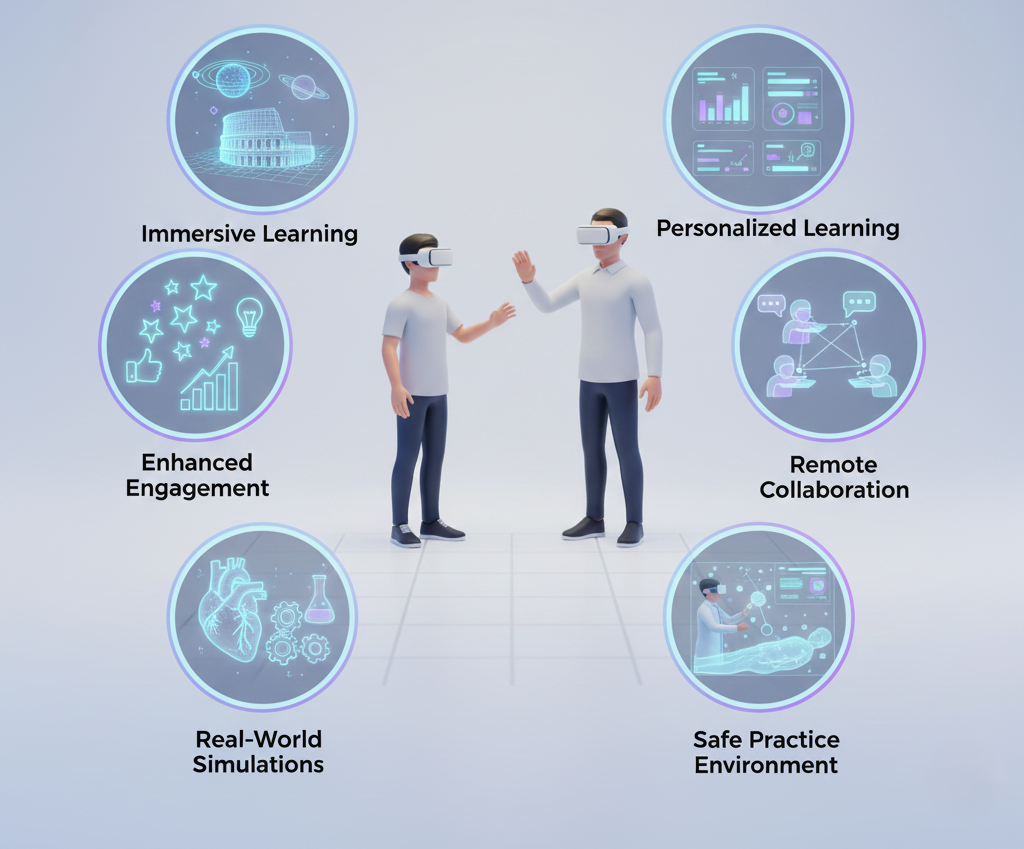
6. Benefits of AR and VR to Students and Educators
The integration of AR and VR in education unlocks numerous benefits that extend across learning outcomes, teaching methods, and classroom efficiency.
1) Higher Engagement and Motivation: Immersive experiences naturally capture learners’ attention and inspire curiosity.
2) Better Knowledge Retention: Studies show that experiential learning improves long-term retention by turning information into active experiences rather than passive memorization.
3) Personalized Learning: AR and VR systems can adapt to complexity, pace, and difficulty according to individual learning needs.
4) Safe Practice Environments: VR allows learners to practice complex tasks without physical risks or resource limitations.
5) Real-time Feedback: Interactive simulations provide instant performance evaluations, helping students learn faster.
6) Improved Teacher Tools: Educators gain powerful platforms for delivering content creatively and assessing student progress.
7) Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice: AR/VR makes abstract concepts concrete and accessible.
7. AR and VR Tools Transforming Today’s Classrooms
Modern classrooms are increasingly adopting immersive technologies using tools such as:
- Google Expeditions VR for virtual field trips
- Interactive AR lessons with Microsoft HoloLens
- Merge Cube for handheld AR 3D models
- Labster VR for virtual science labs
- Tilt Brush/Gravity Sketch to design creatively in VR
- CoSpaces Edu for student-created AR/VR content
These platforms empower teachers and students to create, explore, and learn with immersive experiences tailored to curriculum objectives.
8. The Role of AR/VR in Personalized and Adaptive Learning
Personalized learning is essential in the modern education system, and AR/VR technologies are perfectly aligned to support it.
- Individual Learning Paths: Students can explore lessons at their own pace, revisiting complex topics as needed.
- Adaptive Difficulty: AI-driven AR/VR platforms adjust challenges based on performance.
- Real-Time Insights: Educators gain precise data on student interactions, helping tailor support where needed.
- Reducing Learning Anxiety: Safe, immersive environments build confidence, especially for students who struggle with traditional methods.
AR and VR help create learner-centered environments that support inclusivity and accessibility.
9. Challenges and Limitations of AR and VR in Education
Regardless of their potential, the adoption of AR and VR faces challenges:
1) Cost Barriers: High-quality VR headsets and AR tools can be expensive for some institutions.
2) Technical Requirements: Schools need sufficient bandwidth, hardware, and maintenance resources.
3) Teacher Training: Educators need to be trained to effectively integrate immersive technologies.
4) Car Sickness and Discomfort: Some learners may feel a little discomforted using VR for too long.
5) Availability of Content: High-quality, curriculum-aligned immersive content is on the increase but not yet universal.
Addressing these challenges requires strategic investment, training, and long-term planning.
10. Future Trends Driving AR/VR Innovations in Learning
The future of immersive learning is rich in innovation. Some key trends include:
- Immersive Learning-Powered AI: AI will personalize AR/VR experiences based on learner behavior and performance.
- Mixed Reality Classrooms: In hybrid classrooms, AR, VR, and traditional learning will blend rather seamlessly.
- Haptic Feedback: VR experiences will also become more real with touch-based interactions.
- Immersive Learning Cloud-Based: Cloud platforms will make AR/VR accessible without expensive hardware.
- Gamification and Interactive Assessments: Immersive games and interactive exams are going to make assessment more engaging.
- Global Collaborative Learning: The world’s students will learn together in shared virtual classrooms.
- Greater Penetration into Professional Training: Healthcare, engineering, aviation, retail, and manufacturing industries will rely heavily on VR simulations for workforce training.
The future promises deeper integration of immersive technologies to prepare learners for real-world challenges.
11. Conclusion
AR and VR represent the next evolution of learning from one that emphasizes immersive experiences, personalized pathways, and practical skills. These technologies break the boundaries of traditional education, offering dynamic, interactive, and meaningful experiences that prepare students for the digital age. While challenges remain, the benefits far outweigh the barriers. As innovation continues and adoption grows, AR and VR will become essential components of modern education from classrooms to training centers and beyond.
Immersive learning is no longer a distant possibility. It is the future of education. AR and VR are shaping a world where learning is engaging, accessible, experiential, and powerful, paving the way for a new generation of learners empowered by technology.




