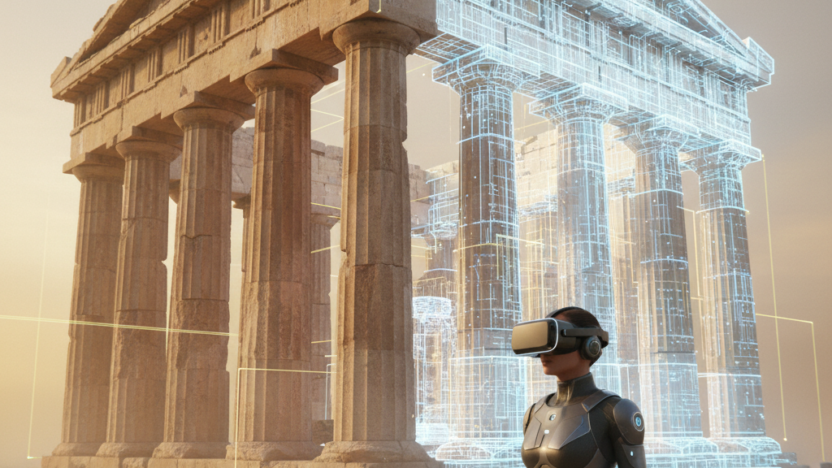
Virtual Reality is revolutionizing the way we preserve and experience ancient history. Through advanced 3D scanning, digital modeling, and immersive simulations, VR allows experts to rebuild monuments that have been damaged, destroyed, or eroded by time. These virtual recreations would give historians, archaeologists, and the public an unparalleled opportunity to explore lost structures in their original state.
From walking through ancient temples to examining minute architectural details, VR brings the past to life in a most vividly accurate manner.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Virtual Reality in Cultural Preservation?
- How VR Reconstructs Ancient Monuments
- Technologies Behind VR Heritage Restoration
- The Role of 3D Scanning and Photogrammetry
- Case Studies: Iconic Monuments Recreated in VR
- Benefits of VR for Historians, Archaeologists, and Educators
- Public Engagement: Bringing Ancient Worlds to Modern Audiences
- Challenges in VR-Based Heritage Reconstruction
- Future Trends in VR for Cultural Preservation
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
For centuries, our understanding of ancient civilizations has depended on what time has kindly left behind fragments of ruined temples, weathered statues, half-buried foundations, and historic sites that erosion, conflict, and natural disasters have slowly erased.
Virtual Reality (VR) has stepped into the world of cultural heritage as one of the most powerful tools we’ve ever had. It’s reconstructing lost monuments, reviving ancient cities, and preserving global heritage in ways traditional restoration cannot. VR allows us to visit historically accurate environments that no longer physically exist. We’re not just reading history anymore; we’re experiencing it firsthand.
This blog explores how VR is transforming cultural preservation, the groundbreaking technologies behind these reconstructions, and the remarkable projects already bringing the ancient world back to life.
2. What is Virtual Reality in Cultural Preservation?
In cultural preservation, VR refers to using immersive digital environments to recreate historical places, artifacts, and events. These reconstructions can be explored through VR headsets, interactive installations, museum exhibits, and even online platforms.
There are three major goals for VR in cultural heritage:
- Preservation: Digitally saving environments and monuments that are at risk or already lost.
- Education: Allowing students, researchers, and the public to step into historical worlds.
- Engagement: To make history accessible, interactive, and emotionally resonant.
3. How VR Reconstructs Ancient Monuments
VR reconstruction typically follows steps like these:
1) Gathering Information from the Past: Historians, archaeologists, and researchers gather everything available for blueprints, photographs, old records, excavation data, and expert interpretations.
2) Scanning and Modeling: 3D scans, drones, and photogrammetry capture the remaining structures.
3) Texturing and Detailing: Textures are created to match the original materials stone, marble, paint, carvings based on archaeological evidence.
4) Simulating Realistic Lighting: Lighting algorithms help recreate how these places look under ancient daylight, torches, or moonlight.
5) Creation of VR Environment: The monument is placed into a virtual world where users can walk, explore, interact, and sometimes even engage with historical narratives.
6) Adding Audio, Narrative, and Interaction: Ambient sounds, narrations, characters, and animations transform the scene into a fully immersive historical experience.
4. Technologies Behind VR Heritage Restoration
Recreating ancient worlds with near-photorealistic accuracy requires several advanced technologies working together. Each one plays a unique role in turning old stones and ruins into vivid virtual experiences.
1) 3D modeling and digital reconstruction software: Tools like Blender, Unreal Engine, Unity, and Autodesk Maya allow artists to sculpt monuments digitally.
2) AI-Assisted Reconstruction: Artificial Intelligence helps fill gaps where historical data is limited by analyzing patterns, architectural styles, and archaeological knowledge.
3) LIDAR Scanning: Laser-based scanning captures precise measurements of ruins and landscapes at sub-millimeter accuracy.
4) Drone Imaging: Drones yield an aerial view of a huge archaeological site and high-resolution images.
5) VR Engines: Platforms like Unreal Engine power in final immersive environment, allowing users to explore the reconstructed world.
6) Motion Capture and Animation: For projects that include historical characters or reenactments, motion capture adds lifelike movement to the experience.
Together, these technologies form a powerful toolkit that pushes the boundaries of cultural preservation.
5. 3D Scanning and Photogrammetry: How They Work
Among all the technologies driving VR heritage reconstruction, 3D scanning and photogrammetry are true game changers.
What is photogrammetry?
It’s a process that turns 2D images into 3D models. By taking hundreds or thousands of photos from different angles, software can recreate a monument with striking accuracy.
Where It’s Used
- Ancient Temples
- Sculptures and artifacts
- Archaeological excavation sites
- Buildings affected by war or natural calamities
6. Case Studies: Iconic Monuments Recreated in VR
Here are some real examples of monuments brought back to life through virtual reconstruction.
1) The Parthenon in Athens: Through photogrammetry and scholarly input, VR recreations show how the Parthenon once looked to be complete with vibrant paint, detailed sculptures, and intact columns.
2) Egyptian Tombs: VR allows us to explore ancient tombs, hieroglyphics, and burial chambers without risking damage to fragile artifacts.
These projects highlight VR’s ability to transform ruins into living historical environments.
7. Advantages of Virtual Reality for Historians, Archaeologists, and Educators
Historians
- Helps test theories by visualizing ancient structures in 3D.
- It gives context to how monuments fit in with everyday life and geography.
Archaeologists
- Allows virtual excavation layers and reconstructions.
- Preserves fragile sites digitally for future research.
- Offers a safe way to analyze dangerous or inaccessible locations.
Educators
- Makes history interactive and interesting.
- Places students inside historical narratives to improve student retention.
- Offers virtual field trips to global sites at minimal cost.
- VR transforms learning from passive reading into active exploration to make history feel alive.
8. Public Engagement: Bringing Ancient Worlds to Modern Audiences
For the public, VR provides unparalleled access to global heritage. You don’t need to fly across the world or hike through remote deserts to experience ancient wonders anymore.
VR makes history accessible
Various VR experiences in museums and cultural centers could now allow visitors to:
- Walk inside lost temples
- Watch historical reenactments
- Explore reconstructed cities
- Be involved with ancient tools and artifacts
- Emotional Impact
Standing inside a lost monument creates a sense of connection that photos and textbooks simply cannot match. People leave VR experiences with a deeper appreciation for the past and a greater desire to preserve cultural heritage.
9. Challenges in VR-Based Heritage Reconstruction
With powerful possibilities come several challenges with VR.
- Gaps in Historical Knowledge: Not everything is known about ancient monuments, leading to reconstruction debates.
- High Cost and Technical Requirements: VR projects require skilled developers, artists, archaeologists, and powerful hardware.
10. Future Trends in VR for Cultural Preservation
The future of VR-based heritage reconstruction is incredibly promising. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
- AI-Driven Reconstruction: AI will help fill historical gaps with more accurate predictions based on architectural patterns and cultural analysis.
- Cloud-based heritage archives: Monuments and artifacts will be stored in massive global digital libraries, accessible from anywhere.
- Multi-User Virtual Worlds: Imagine entire classes exploring ancient civilizations together in shared VR environments.
- Haptic Feedback Integration: Future VR may allow users to “touch” ancient surfaces and materials through advanced haptic systems.
- Digital Twin Technology: Sites will be updated in real time with environmental and structural data, creating living digital replicas of heritage locations.
The future holds even deeper immersion, higher accuracy, and broader accessibility.
11. Conclusion
From ancient temples to vanished cities, VR allows us to reconnect with lost heritage in ways that are immersive, educational, and emotionally powerful.
As technology continues to advance, the digital resurrection of ancient monuments will only become more accurate, more accessible, and more transformative.




