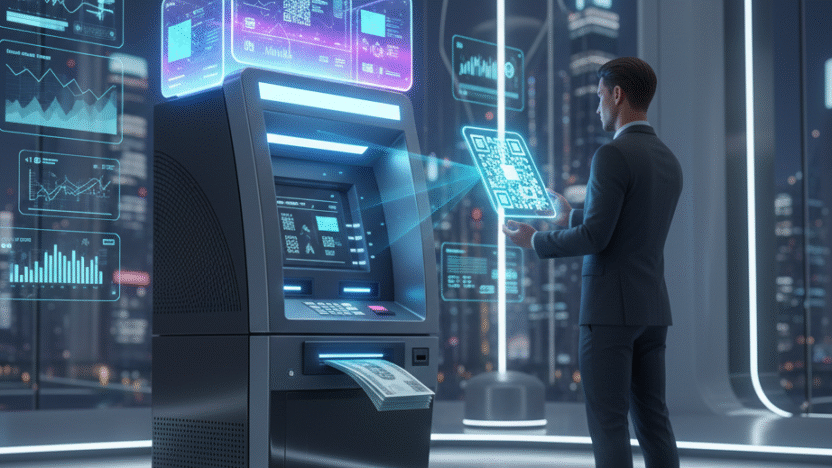
It explores how modern banking is evolving beyond traditional cards to offer faster, safer, and more convenient access to cash. With innovations like mobile authentication, QR codes, and biometric verification, customers can now withdraw money securely without physical cards. This technology not only enhances user convenience but also reduces the risk of fraud and card loss.
As financial institutions embrace digital transformation, cardless withdrawals are becoming a cornerstone of smart, seamless banking. The future of banking lies in accessibility, efficiency, and security for all driven by cutting-edge, cardless innovations.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How Cardless Cash Withdrawal Works
- Key Technologies Behind Cardless Banking
- Benefits of Cardless Cash Withdrawal
- Use Cases in Modern Banking
- Security Measures and Fraud Prevention
- Impact on Customer Experience and Convenience
- Role of Banks in Promoting Digital Transactions
- Challenges and Limitations of Cardless Systems
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
The world of banking has been undergoing a massive digital transformation over the past decade, revolutionizing the way customers interact with financial institutions. Among the many innovations reshaping modern banking, cardless cash withdrawal stands out as one of the most significant advancements. This technology allows users to withdraw money from ATMs without needing a physical debit or credit card. Instead, withdrawals can be completed using mobile apps, QR codes, biometric authentication, or one-time PINs generated digitally.
The shift toward cardless transactions is rooted in rapid technological enhancements, customer demand for convenience, and the growing need for more secure banking alternatives. With the rise of mobile banking and digital wallets, customers are increasingly comfortable using smartphones as their primary banking interface. As a result, the traditional plastic card once considered an essential tool for accessing cash is becoming optional.
Cardless withdrawals address a variety of modern challenges, such as card theft, skimming fraud, and misplaced or forgotten cards. By leveraging digital authentication methods, banks can offer a secure and seamless withdrawal experience. The concept is also aligned with global trends toward contactless services, accelerated heavily by the COVID-19 pandemic, which pushed consumers and businesses to prioritize hygiene and avoid unnecessary physical contact.
2. How Cardless Cash Withdrawal Works
While cardless cash withdrawal processes may vary slightly across banks and regions, the underlying mechanisms remain consistent. The goal is to allow customers to authenticate themselves through digital means instead of relying on a plastic card. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the system typically works:
2.1 Initiation Through Mobile Banking App
The customer initiates a cash withdrawal request using their bank’s mobile app. Within the app, they select the “Cardless Withdrawal” option and specify the withdrawal amount. The bank then generates a secure code, QR code, or one-time PIN (OTP) associated with the request.
2.2 Verification of Identity
Before generating the withdrawal code, the bank verifies the user’s identity with one or several security methods:
- Password/PIN
- Biometric verification (fingerprint, facial recognition)
- Device-based authentication
- Two-factor authentication (2FA)
This ensures that the withdrawal process begins only after confirming that the user is genuinely authorized.
2.3 Code Generation
Once authenticated, the bank generates:
- A QR code
- A one-time PIN
- A unique token
- A withdrawal reference number
This code remains valid for a limited time—usually between 5 to 30 minutes to prevent misuse.
2.4 ATM Interaction
At the ATM, the user selects “Cardless Withdrawal” or a similar option. Depending on the bank and ATM technology, the user may:
- Scan the QR code using the ATM scanner
- Enter the unique PIN or token
- Authenticate biometrically through an ATM equipped with fingerprint or face recognition
2.5 Withdrawal Approval
The ATM communicates with the bank server to confirm the code’s validity. Once confirmed, the machine dispenses the requested amount, completing the transaction without a physical card.
2.6 Transaction Completion
The mobile app instantly receives a notification confirming the transaction. If the user fails to complete the withdrawal in time, the code expires, and the transaction is canceled automatically.
3. Key Technologies Behind Cardless Banking
Cardless cash withdrawal systems rely on a combination of advanced technologies that work together to ensure speed, accuracy, and high security. Here are the key technologies powering cardless banking:
3.1 Mobile Banking Platforms
Mobile apps serve as the command center for cardless withdrawals. They provide:
- Real-time transaction authentication
- Code generation
- Secure communication with bank servers
- Push notifications for user confirmation
Modern mobile apps integrate biometric security and encrypted data transfer to protect user information.
3.2 QR Code Technology
QR codes have become a universal tool for digital interactions. They’re secure, easily generated, and simple to scan at ATMs. QR codes minimize errors, reduce the need for manual input, and support fast processing.
3.3 Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive card data with a temporary token. For example, instead of transmitting actual card details, the system uses a digital token linked to the withdrawal request, protecting the user’s financial information.
3.4 Biometrics
Biometric systems are like fingerprint and facial recognition and offer an ultra-secure method of verifying user identity. They eliminate the risk of PIN theft and enhance overall security.
3.5 Cloud Computing
Cloud-based servers support real-time data processing, allowing banks to manage cardless transactions efficiently. Cloud infrastructure helps maintain uptime, scalability, and rapid communication between mobile apps and ATMs.
3.6 NFC (Near-Field Communication)
NFC-enabled cardless withdrawals allow users to tap their phones on NFC-ready ATMs. This technology is like contactless payments and is highly secure due to localized communication between devices.
3.7 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI/ML algorithms help detect fraudulent or suspicious behavior during cardless withdrawals. They analyze patterns such as transaction time, location, user behavior, and device recognition.
4. Benefits of Cardless Cash Withdrawal
Cardless withdrawal offers a range of advantages for both customers and financial institutions. These benefits are driving increased adoption across global banking systems.
1) Enhanced Security: Traditional debit and credit cards are vulnerable to skimming, theft, and cloning. Cardless withdrawals eliminate these risks by relying on secure digital methods.
2) Convenience and Speed: Users can withdraw cash without carrying a wallet or card, reducing the hassle of misplaced cards. The process is faster since users skip PIN entry or card insertion.
3) Reduced Fraud: Digital authentication methods, including biometrics and OTPs, significantly lower fraud attempts. Tokenized codes are nearly impossible to replicate.
4) Contactless Transactions: Especially post-pandemic, customers prefer contactless methods for hygiene and safety. Cardless withdrawals reduce physical interaction with ATM surfaces.
5) Emergency Access to Cash: Users who lose, misplace, or forget their physical cards can still access cash instantly. Families can also send cardless withdrawal codes to loved ones in emergency situations.
6) Lower Cost for Banks: Banks save costs related to physical card printing, replacement, and maintenance. Digital processes streamline operations and reduce long-term operational expenses.
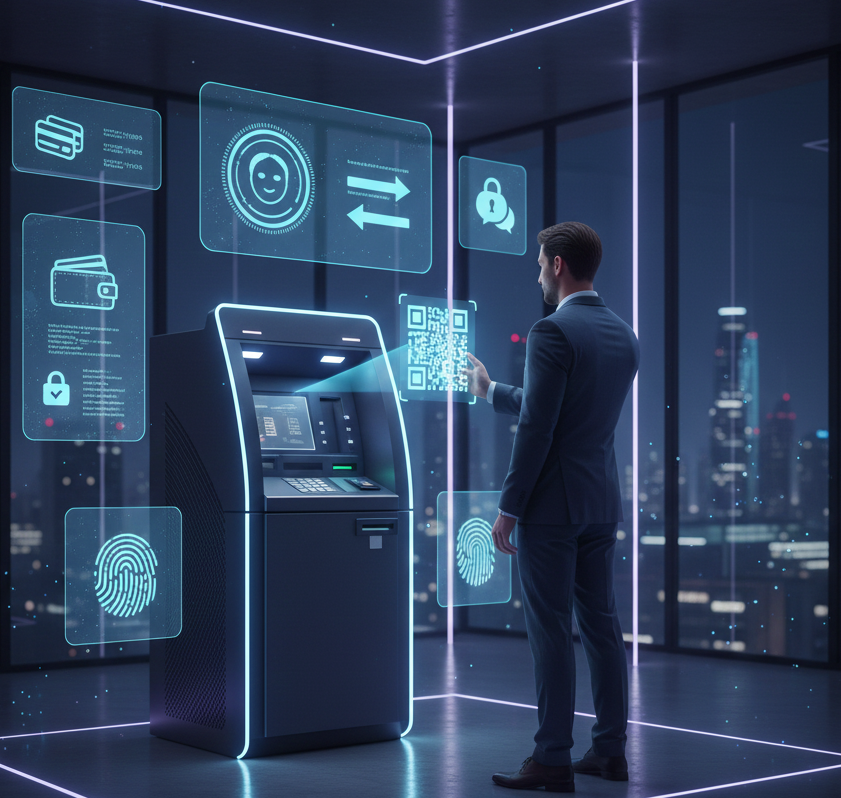

5. Use Cases in Modern Banking
Cardless cash withdrawals are becoming popular across a wide range of scenarios:
1) Lost or Stolen Card Situations: Users can instantly withdraw cash even without their card, preventing disruptions.
2) Remote Cash Transfers: Individuals can send withdrawal codes to family members, allowing them to pick up cash at an ATM without needing a bank account.
3) Business Operations: Companies can issue secure withdrawal tokens to employees for specific tasks such as emergency cash purchases or outstation expenses.
4) Tourist and Travel Convenience: Travelers often face issues with card compatibility or ATM malfunctions. Cardless withdrawals simplify international travel by offering easy access to funds.
5) Banking for Unbanked Populations: Some banks allow coded withdrawal options for users without permanent bank accounts, supporting financial inclusion.
6) Contactless Banking Solutions: As digital-first banking becomes the norm, cardless withdrawals fit perfectly with contactless service strategies.
6. Security Measures and Fraud Prevention
Security is the backbone of cardless withdrawal systems. Banks implement several safeguards such as:
1) Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Every withdrawal involves at least two verification steps, making unauthorized access extremely difficult.
2) Time-Sensitive OTPs: Each OTP or token expires within minutes, significantly reducing fraud risk.
3) Geo-Location Tracking: Banks track the user’s device location during code generation to prevent suspicious withdrawal attempts.
4) Biometric Verification: Biometrics offer an additional layer of protection that prevents even device theft from compromising accounts.
5) AI-Based Fraud Detection: AI analyzes user behavior and flags abnormal activities such as unusual withdrawal locations or repeated failed attempts.
7. Impact on Customer Experience and Convenience
Cardless withdrawals significantly elevate the modern banking experience. Customers enjoy:
1) Faster and Smoother Transactions: The elimination of physical card handling reduces steps and speeds up the process.
2) Higher Flexibility: Users can withdraw cash anytime without relying on a card.
3) Enhanced Accessibility: Elderly or impaired users benefit from the simplicity of QR-code or biometric-based withdrawals.
4) Improved Digital Banking Engagement: Customers interact with mobile apps more often, leading to a more connected banking experience.
5) Personalized Banking: Banks can integrate rewards, analytics, and budgeting tools into the mobile app, enriching the customer journey.
8. Role of Banks in Promoting Digital Transactions
Banks play a pivotal role in advancing cardless withdrawal systems. Their responsibilities include:
1) Investing in Digital Infrastructure: Developing advanced ATM networks and mobile applications is essential.
2) Educating Customers: Banks must launch awareness campaigns to explain the benefits and safety of digital withdrawals.
3) Enhancing System Interoperability: Ensuring seamless compatibility between ATMs and mobile systems increases adoption rates.
4) Partnering with Fintech Companies: Collaborations with fintech firms accelerate innovation and bring new features faster to customers.
9. Challenges and Limitations of Cardless Systems
Despite the many advantages, cardless withdrawal systems face certain challenges:
1) ATM Limitations: Not all ATMs support QR codes, NFC, or mobile-based withdrawal options.
2) Internet Dependence: Cardless withdrawals require stable internet connectivity for app authentication.
3) Technical Glitches: System downtime or app malfunctions may interrupt withdrawal access.
4) Higher Implementation Costs Initially: Banks must upgrade ATM hardware and digital systems before adopting cardless technologies widely.
10. Conclusion
Cardless cash withdrawal is more than just a modern convenience. It represents a significant step toward the future of digital banking. As consumer behavior shifts toward mobile-first interactions and contactless transactions, cardless withdrawals offer a secure, fast, and reliable alternative to traditional ATM methods. With robust technologies like biometrics, AI-driven security, QR codes, and mobile authentication, this system is set to become the new standard in global banking.
Banks that embrace this innovation early will gain a competitive advantage and offer customers unmatched convenience while enhancing digital engagement. While challenges exist, the benefits far outweigh the limitations of positioning cardless withdrawals as a cornerstone of the future banking experience.