Marketing plays a crucial role in the success of any business by creating awareness, generating leads, and driving customer engagement. This guide delves into the core concepts of marketing, offering a clear understanding of how marketing functions within a business context. It explores key strategies used to attract and retain customers, such as digital marketing, content marketing, and relationship marketing, as well as various marketing types that suit different business goals.
Whether you’re a startup or an established company, understanding these strategies and types can help you build a strong brand presence, reach the right audience, and grow your business effectively.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Marketing?
- The Role of Marketing in Business
- Core Components of Marketing
- Types of Marketing
- Key Marketing Strategies
- B2B vs B2C Marketing Approaches
- Emerging Trends in Marketing
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
- In today’s dynamic and highly competitive business environment, marketing is no longer optional. Whether you’re launching a startup, scaling an established company, or entering new markets, marketing plays a critical role in shaping the success and sustainability of your business. It’s more than just advertising or selling; marketing is a strategic function that connects businesses with their customers, builds brand awareness, drives sales, and cultivates loyalty.
- Understanding the fundamentals of marketing along with the wide array of strategies and types available is key to making informed decisions and crafting campaigns that truly resonate with your target audience. From traditional channels like print and radio to modern digital platforms like social media and AI-powered personalization, businesses today have an unprecedented toolkit at their disposal.
- This blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of marketing in business. We’ll explore the core components of effective marketing, examine various types of marketing approaches, and break down key strategies that can be tailored to different business goals. Whether you’re new to marketing or looking to refine your existing efforts, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to navigate and succeed in the evolving world of business marketing.
2. What is Marketing?
Marketing is the strategic process through which businesses identify, attract, engage, and retain customers by delivering value. At its core, marketing is about understanding the needs and desires of your target audience and crafting messages, products, and experiences that fulfill those needs better than the competition.
More than just advertising or sales, marketing encompasses a wide range of activities.
- Market research to understand consumer behavior and trends.
- Product development based on customer needs.
- Branding and positioning to shape perception and recognition.
- Promotion and communication to inform and persuade potential buyers.
- Distribution and placement to ensure products are available where and when needed.
- Customer relationship management to maintain loyalty and advocacy.
3. The Role of Marketing in Business
Marketing is the engine that drives a business forward. It plays a central role in connecting a company with its customers, shaping public perception, influencing behavior, and generating revenue. In the modern business landscape, marketing extends far beyond traditional advertising. It is embedded in nearly every function of a successful enterprise.
1) Building Brand Identity and Recognition
One of marketing’s most powerful functions is brand building. Through consistent messaging, visual identity, and emotional appeal, marketing establishes how a business is perceived by its audience.
- Builds trust and credibility
- Differentiates a business from competitors
- Enhances customer loyalty
2) Understanding and Meeting Customer Needs
At the heart of effective marketing is a deep understanding of customer behavior. Market research, surveys, customer data, and analytics enable businesses to:
- Identify target segments
- Understand consumer pain points
- Develop products and services that meet real needs
3) Driving Revenue and Profitability
Marketing has a direct impact on the bottom line. Strategic marketing initiatives such as promotional campaigns, search engine optimization, and lead nurturing are designed to:
- Generate demand
- Attract qualified leads
- Convert prospects into paying customers
4) Supporting Sales and Business Development
While sales and marketing are distinct functions, they work together. Marketing creates awareness and interest, while sales close the deal.
- Provide sales teams with qualified leads
- Develop sales enablement materials (brochures, case studies, email templates)
- Create messaging that resonates with prospects
4. Core Components of Marketing
Marketing is a multifaceted discipline composed of several interconnected components that together drive a business’s ability to reach and influence its target audience. Understanding these core components is essential for building a successful marketing strategy that aligns with business goals and resonates with customers.
1) Market Research
Market research is the foundation of all marketing activities. It involves gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market.
- Customer preferences and behaviors
- Industry trends
- Competitive landscape
- Market demand
2) Target Audience Identification
Knowing who you’re marketing to is as important as what you’re marketing. Identifying and understanding your target audience allows you to segment the market and focus your efforts on the groups most likely to convert.
- Demographics (age, gender, income)
- Psychographics (interests, lifestyle, values)
- Behavioral data (purchasing habits, brand interactions)
- Geographics (location, climate, urban/rural)
3) Branding
Branding is the process of creating a unique identity for your business. It encompasses everything from your logo and color scheme to your tone of voice and brand story.
- Builds recognition and trust
- Sets expectations for product quality and service
- Differentiates you from competitors
4) Marketing Channels
Choosing the right channels to communicate with your audience is vital. The optimal mix depends on your target market, budget, goals, and message.
- Online: Websites, social media, email, search engines
- Offline: TV, radio, print ads, billboards
- Hybrid: Events, QR codes, cross-channel promotions
5) Content Creation
Content is the vehicle through which marketing messages are delivered. High-quality content educates, informs, entertains, or persuades your audience.
- Blog posts and articles
- Videos and podcasts
- Infographics and eBooks
- Case studies and testimonials
6) Promotion and Communication
Promotion encompasses the various tactics used to inform, persuade, and remind the target audience about your brand or product. This includes:
- Advertising (digital and traditional)
- Public relations (press releases, media outreach)
- Social media engagement
- Sales promotions and discounts
5. Types of Marketing

Marketing has evolved dramatically over the years, adapting to technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and shifting business environments. Today, businesses have access to a wide variety of marketing types, each suited to different goals, audiences, and contexts.
1) Traditional Marketing
Traditional marketing refers to offline promotional methods that were widely used before the digital era. These methods still play a significant role in reaching broad or local audiences.
Examples:
- Television and radio ads
- Newspaper and magazine ads
- Billboards and posters
2) Digital Marketing
Digital marketing uses the internet and digital platforms to promote products and services. It offers measurable, targeted, and cost-effective solutions compared to traditional methods.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – improving visibility in organic search results
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) – paid advertising on platforms like Google Ads
- Display advertising – visual banner ads on websites
3) Content Marketing
Content marketing focuses on creating valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience. Rather than directly promoting a brand, content marketing builds trust and authority.
- Blog posts and articles
- E-books and whitepapers
- Videos and tutorials
4) Social Media Marketing
This type of marketing uses social platforms to connect with audiences, increase brand visibility, and drive engagement.
- X (formerly Twitter)
5) Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing involves collaborating with individuals who have a strong online following to promote products or services to their audience. It leverages trust and credibility built between the influencer and their followers.
Types of influencers:
- Mega (celebrities)
- Macro (100k–1M followers)
- Micro (10k–100k followers)
- Nano (1k–10k followers)
6) Email Marketing
Email marketing is a direct and highly personal way to communicate with current and potential customers. It’s used to nurture leads, retain customers, and promote offers.
- Newsletters
- Welcome sequences
- Product updates
- Abandoned cart reminders
- Promotional campaigns
7) Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based strategy where external partners (affiliates) promote a company’s products in exchange for a commission on sales generated through their links.
- Low upfront cost
- Performance-driven
- Expands reach without heavy investment
8) Mobile Marketing
Mobile marketing targets users on their smartphones or tablets through SMS, mobile apps, or mobile-friendly content.
- In-app advertising
- Mobile-responsive websites
- Text message campaigns
- Location-based promotions
9) Video Marketing
Video marketing uses short or long-form video content to engage users and explain products or services more effectively.
- YouTube
- Instagram Reels
- Brand websites
6. Key Marketing Strategies
While the types of marketing define how and where you reach your audience, marketing strategies define what you say, to whom, when, and why. A marketing strategy is a long-term plan that outlines the path to achieving a brand’s marketing goals, from positioning to conversion.
1) Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves dividing a broad target market into smaller, more manageable groups of consumers who share similar characteristics. These characteristics can include demographics, behaviors, needs, or psychographics.
Benefits:
- More personalized messaging
- Better product-market fit
- Higher engagement and conversion rates
2) The 4 Ps of Marketing
Also known as the Marketing Mix, the 4 Ps provide a framework for executing marketing strategy:
- Product: What are you offering? What need does it satisfy?
- Price: What is its value? How does pricing affect perception?
- Place: Where and how is the product available?
- Promotion: How will you communicate its value to the market?
3) Inbound vs. Outbound Marketing
Inbound Marketing focuses on attracting customers through valuable content and organic engagement. It’s about earning attention.
Techniques include:
- Blogging
- SEO
- Social media
- Ebooks and guides
- Webinars
4) Data-Driven Marketing
In data-driven marketing, decisions are guided by analytics and performance metrics rather than assumptions or intuition. Businesses collect and analyze data to understand:
Tools commonly used:
- Google Analytics
- CRM platforms (like HubSpot, Salesforce)
- Social media analytics
- Marketing automation platforms
5) Value Proposition Strategy
A value proposition defines why a customer should buy from you rather than a competitor. A strong value proposition:
- Communicates clear, unique benefits
- Solves a customer’s problem or fulfills a desire
- Builds emotional or functional connection
6) Growth Hacking
Popular among startups and tech companies, growth hacking is a strategy focused on rapid experimentation across channels and product development to identify the most effective ways to grow a business.
- Referral programs
- Viral loops
- Freemium models
- Landing page optimization
- A/B testing
7. B2B vs B2C Marketing Approaches
Marketing strategies must be tailored to the nature of your audience. One of the most fundamental distinctions in marketing is whether your business serves other businesses (B2B) or individual consumers (B2C). While both aim to generate sales and build brand loyalty, the tactics, messaging, and buying behaviors in each segment differ significantly.
1) Target Audience
B2B (Business-to-Business):
Targets decision-makers within organizations (e.g., CEOs, managers, procurement teams). Purchases are often made by committees or based on logical, budget-driven considerations.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer):
Targets individual consumers or households. Purchasing decisions are often emotional, impulsive, or convenience-driven.
2) Sales Cycle
B2B:
Typically has a longer sales cycle involving research, consultation, demos, and negotiations. The process may take weeks or even months.
B2C:
Usually has a shorter sales cycle, sometimes completed within minutes or hours. The focus is on speed, ease, and satisfaction.
3) Decision-Making Process
B2B:
Decisions are rational and strategic—based on ROI, efficiency, and long-term value. Multiple stakeholders may be involved.
B2C:
Decisions are often emotional and spontaneous, driven by personal preferences, brand perception, or peer influence.
4) Content and Messaging
B2B:
Content is more informative, technical, and value-driven. Examples include whitepapers, case studies, webinars, and detailed product demos.
B2C:
Content is usually entertaining, emotional, or benefit-focused. Examples include social media posts, influencer videos, product reviews, and lifestyle blogs.
5) Marketing Channels
B2B:
- Email marketing
- Industry events and webinars
- Search engine marketing (SEM)
- Account-based marketing (ABM)
B2C:
- Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, YouTube
- Influencer partnerships
- Mobile and app-based advertising
- E-commerce platforms
- SMS and email promotions
8. Emerging Trends in Marketing
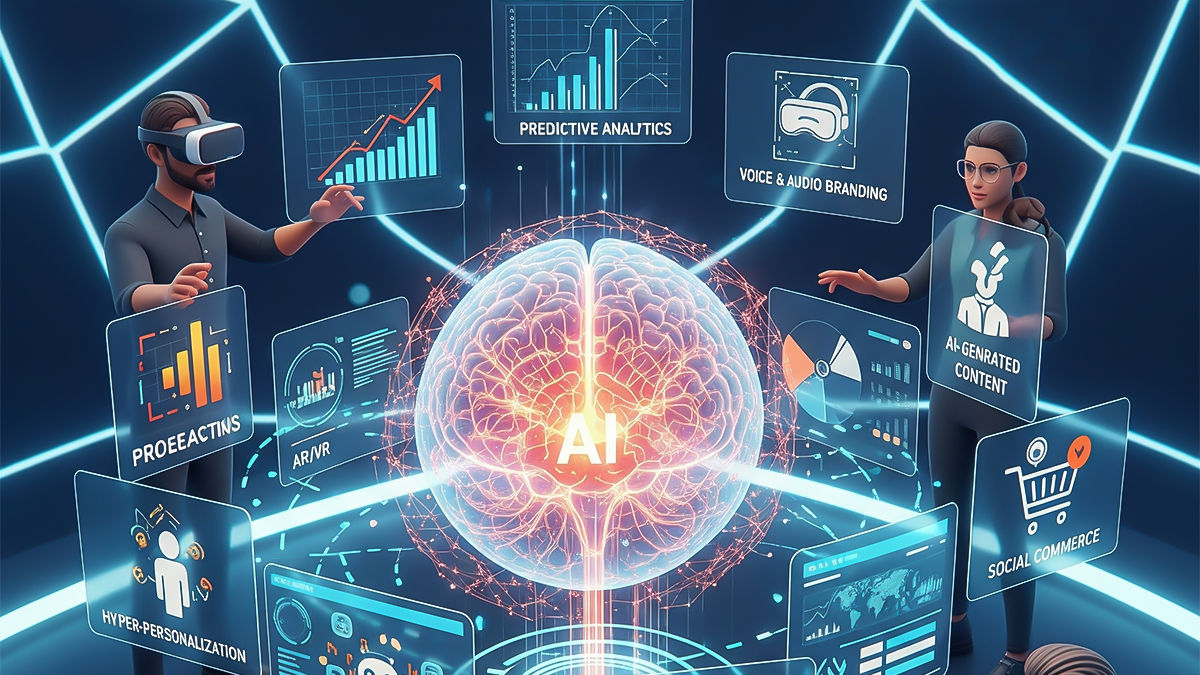

The marketing landscape is constantly evolving, driven by changes in technology, consumer behavior, data accessibility, and cultural shifts. Businesses that stay on top of emerging trends are more likely to capture attention, build deeper customer relationships, and remain competitive in dynamic markets.
1) Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
AI is transforming how marketers analyze data, personalize content, and optimize campaigns. Machine learning algorithms can process massive datasets to predict consumer behavior, improve targeting, and automate repetitive tasks.
Key AI applications in marketing:
- Chatbots for instant customer support
- Predictive analytics for personalized recommendations
- Automated content creation and email sequences
- Dynamic pricing and ad targeting
- Customer sentiment analysis
2) Personalization and Hyper-Targeting
Consumers now expect content and experiences tailored to their preferences, behavior, and history. Personalization goes beyond using a customer’s name. It includes content recommendations, customized offers, and predictive messaging.
3) Voice Search and Smart Devices
As smart assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri become more common, consumers are using voice to search, shop, and make inquiries. This shift demands a new approach to SEO and content.
Voice search characteristics:
- Longer, conversational queries
- Local intent (“near me” searches)
- Mobile-first indexing
4) Video and Short-Form Content Dominance
Video content continues to be one of the most effective ways to engage audiences. With platforms like TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts gaining traction, short-form video is now a dominant format.
Popular formats include:
- Product demos
- Behind-the-scenes content
- User-generated reviews
- Educational or how-to clips
5) Influencer and Creator-Led Marketing
The rise of content creators and influencers has revolutionized brand promotion. Instead of big-budget celebrity endorsements, brands now partner with micro and nano influencers who offer niche relevance and trusted voices.
Emerging trends in influencer marketing:
- Long-term brand ambassadorships
- Co-creation of products or content
- Livestream shopping and real-time engagement
6) Augmented Reality (AR) and Immersive Experiences
AR is being used to bridge the gap between physical and digital experiences. From virtual try-ons to 3D product visualizations, immersive marketing allows customers to interact with products in new ways.
Use cases:
- Furniture companies offering “place-in-room” views (e.g., IKEA Place)
- Beauty brands enabling virtual makeup trials (e.g., L’Oréal, Sephora)
- AR filters and interactive ads on Instagram and Snapchat
9. Conclusion
- Marketing is the lifeblood of any successful business. It’s not just about selling a product or service. It is about understanding customer needs, creating value, and building long-term relationships. From foundational principles to cutting-edge digital innovations, marketing has evolved into a complex, strategic discipline that drives business growth and competitiveness.
- In this blog, we explored what marketing is, it is critical role in business, and the core components that make it effective. We examined a wide range of marketing types from traditional advertising to digital strategies and analyzed key approaches used in both B2B and B2C contexts. We also identified the most impactful marketing strategies and highlighted the emerging trends shaping the future, such as AI, personalization, and immersive technologies.